In 2017, the global Internet of Things (IoT) landscape saw significant developments with both Narrowband IoT and LoRa networks gaining traction. Countries like China and South Korea were at the forefront of this technological shift, with LoRa finding strong partnerships in enterprise-specific solutions, while NB-IoT attracted more attention from telecom operators.
On July 5, according to foreign reports, Samsung announced a collaboration with SK Telecom to roll out the world's first commercial IoT-dedicated LoRaWAN network. This network will operate on the 900 MHz band, with initial business services launching in Daegu, South Korea’s fourth-largest city, starting August.
Meanwhile, China Telecom led the way in IoT infrastructure by establishing a network comprising 310,000 NB-IoT devices by May 29. In July, the company introduced the world’s first NB-IoT tariff plan, focusing on charging for connection services to emphasize connectivity value. Following this, Shenzhen Telecom announced the deployment of the first 6,000 NB-IoT smart gas meters in August. These meters are set to be installed and operational by early September and delivered to residents in October, marking China Telecom as the first operator in China to offer commercial NB-IoT services.
During the 2017 China International IoT and Smart China Summit in Shenzhen on August 16, Dr. Yang Liu, Business Development Director at Semtech, discussed "LoRa Global Business Opportunities and Competitive Analysis." He highlighted the three key advantages of the LoRa network deployment and shared insights into the latest developments within the LoRa ecosystem.
One of the standout features of LoRa technology lies in its ability to address various IoT requirements effectively. While neither NB-IoT nor LoRa can meet all IoT needs, LoRa offers distinct benefits in terms of network cost, data transmission rates, node costs, and deployment flexibility.
Dr. Liu emphasized that LoRa’s adoption of linear frequency modulation spread spectrum modulation technology preserves the low power consumption characteristics of Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) modulation while increasing communication distances. This innovation enhances network efficiency and reduces interference. Additionally, LoRa’s spread spectrum sequencing allows multiple nodes to transmit simultaneously on the same frequency without interfering with one another, enabling Concentrators/Gateways to handle data from numerous nodes concurrently, thereby boosting system capacity.
Semtech unveiled a new chip in August 2013 based on Long Range (LoRa) technology below 1GHz. This chip boasts an impressive reception sensitivity of -148dBm, surpassing other leading sub-GHz chips by over 20dB, ensuring reliable network connections. LoRa’s design also supports long-distance communication with minimal power usage—sleep mode consumes only 2 microamps, standby mode 2mA, reception under 10mA, and transmission at 30mA at 14dB.
These advancements make LoRa particularly attractive for applications requiring extensive range and low power consumption. For instance, tests conducted with a Cisco router demonstrated that LoRa signals could travel over 30 miles (50km) unobstructed between San Jose and San Francisco airports. Such capabilities, coupled with low power consumption, ensure that devices powered by LoRa technology can last up to 10-20 years on a single battery.
In conclusion, both NB-IoT and LoRa present unique opportunities and challenges within the IoT sector. While NB-IoT leverages telecom infrastructure for widespread coverage, LoRa shines through its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. As seen in South Korea and China, these technologies are rapidly shaping the future of IoT globally.
Pure sine ware output
Optional MPPT/PWM solar charge controller 60A
MPPT Efficiency max 98%
DC Start & Automatic Self-Diagnostic Function
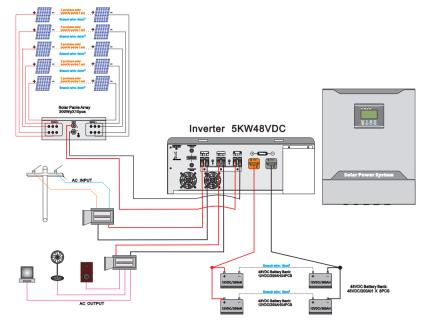
On/Off Grid Solar Inverter,Hybrid Inverter With Mppt Charge,pure sine wave solar inverter
suzhou whaylan new energy technology co., ltd , https://www.whaylan.com