introduction
Lighting system design is the core of road lighting. The ideal lighting scheme not only needs to meet the safety and comfort requirements of pedestrians, but also energy saving and environmental protection. The evaluation indicators [1, 2] involved are very difficult, which makes the establishment of evaluation scheme very difficult. In addition, due to the influence of the surrounding light environment and the influence of the vehicle line, the field test efficiency of the lighting effect parameter value is low, and the measurement accuracy is not high, which also causes inconvenience to the evaluation of the road lighting effect. At present, the research on the comprehensive evaluation method of road lighting system design is still in the exploratory stage. How to obtain the road lighting design index value conveniently and accurately, and then comprehensively evaluate the complex and diverse road lighting effects, which becomes the key to the choice of road lighting design scheme. problem.
1 Lighting road design evaluation model
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a multi-objective and multi-criteria decision-making analysis method. It combines quantitative analysis with qualitative analysis. It has the advantages of structured, well-organized and balanced, and is the project selection, system evaluation and resource allocation. An effective solution to such problems [3-7]. This paper establishes a road lighting scheme evaluation model based on the theory of analytic hierarchy process, as shown in Figure 1. The model consists of four parts: 1) Target layer: The target layer is the ultimate goal of lighting effect evaluation, that is, selecting a more reasonable lighting scheme; 2) The criterion layer: The criterion layer is mainly the influencing factors of the target layer, including the lighting quality and 3 aspects of energy consumption; 3) Index layer: This layer is mainly the evaluation index of lighting effect. Since the elements of this layer are in principle irrelevant, there is a correlation between brightness and illuminance index and brightness uniformity and illuminance uniformity. The two can only take one; 4) Solution layer: This layer is mainly designed for different road lighting. Based on the above analysis, the hierarchical structure of the lighting scheme evaluation is established.
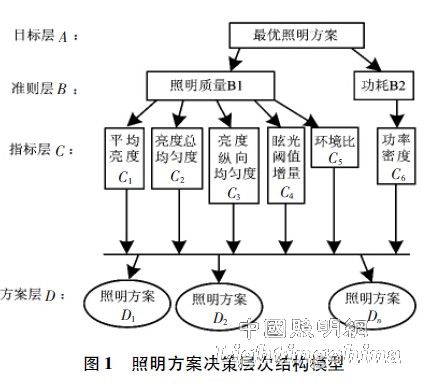
2 Road lighting design evaluation method
2. 1 Determination of the judgment matrix of the influence factor of the lighting scheme evaluation
After establishing the hierarchical structure of the lighting scheme evaluation, the relative importance of the factors to the upper level factors is compared in pairs, and the judgment matrix is ​​established according to the 1~9 scale [8] proposed by Satty TL. , its meaning is shown in Table 1. For example, the criterion layer B establishes a judgment matrix A = [aij] n × n with respect to the target layer A, where aij is the relative importance scale of the i-th factor of the level B compared with the j-th factor for the previous level A. degree.
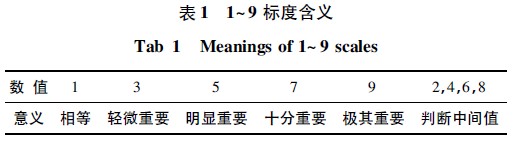
2. 2 hierarchical single sorting and consistency check
The priority of the factors in the criterion layer B relative to the target layer A is calculated by the judgment matrix A = [aij] n × n, and then these weights constitute a single-ordered vector indicating the priority order of the B-layer factors. The calculation of the hierarchical single sort vector can be summarized as solving the eigenvector W corresponding to the maximum eigenvalue of the matrix A. In this paper, we use the first row of the judgment matrix to find the root and normalization method, such as (1) and (2), and then we can obtain the maximum eigenvalue of matrix A from equations (1), (2), and (3). .
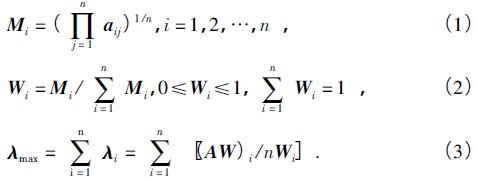
Similarly, the single order vector of the index level C and the maximum eigenvalue of the matrix B can be obtained by judging the matrix B.
Because there are subjective differences in the judgment matrix determined by the pairwise comparison, there is a risk of self-contradictory judgment matrix, and it is necessary to test the consistency. According to CI = ( λmax - n) / ( n - 1) , CR = CI / RI calculate the consistency index CI of the judgment matrix, the random consistency index CR (RI is the average random consistency index, which can be obtained by looking up the table), Hierarchical single sort consistency check. If CR = 0, the judgment matrix has complete random consistency; if CR < 0. 1, the judgment matrix has satisfactory random consistency; if CR > 0. 1, the judgment matrix needs to be adjusted.