**First, Resistor Code: R**
A resistor is a fundamental electronic component that limits the flow of electric current in a circuit. It is commonly used to control the amount of current passing through a specific branch of the circuit. The symbol for a resistor is typically represented as a zigzag line.
**Function**: Resistors are used for current limiting, voltage division, power dissipation, and providing stability in circuits. They can also be used for signal filtering and biasing in amplifiers.
**Testing**: To determine if a resistor is good or bad, use a multimeter to measure its resistance value. The measured value should be close to the nominal value or within the tolerance range (usually ±5% or ±10%). If the resistor is burned out, it may appear blackened or charred. A reading lower than the nominal value could indicate a shorted or damaged resistor.
**Units**: Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω), kilohms (kΩ), and megohms (MΩ).
---
**Second, Capacitor Code: C**
A capacitor is an electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It is usually denoted by the letter "C" followed by a number. Capacitors can be polarized (e.g., electrolytic) or non-polarized (e.g., ceramic). Polarized capacitors have a positive and negative terminal, with longer leads indicating the positive side.
**Features**: One of the key properties of a capacitor is that it blocks direct current (DC) while allowing alternating current (AC) to pass.
**Function**: Capacitors are widely used for coupling, decoupling, filtering, energy storage, and timing circuits. They are also used in power supplies for smoothing voltage fluctuations.
**Testing**: To check a capacitor, first discharge it by shorting its terminals. Then, use a multimeter in resistance mode. If the needle swings and returns to its original position, the capacitor is likely good. If it doesn’t move, it may be open. If it stays at a low resistance, it might be shorted. For small capacitors, you can use the "electric pen method" or apply an AC signal to test its functionality.
**Construction**: A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating dielectric material.
**Symbol**:

**Voltage Rating**: This indicates the maximum voltage the capacitor can safely handle without breaking down. When replacing a capacitor, the new one should have a voltage rating equal to or higher than the original.
**Capacitance**: The capacitance value determines how much charge the capacitor can store. The opposition to AC current is called capacitive reactance (XC = 1/(2Ï€fC)), which depends on both frequency and capacitance.
---
**Third, Inductor Code: L**
An inductor is a passive component made by winding insulated wire around a core, which can be air, iron, or ferrite. It stores energy in a magnetic field when current flows through it. In circuits, inductors are often labeled as "L" followed by a number.
**Symbol**:
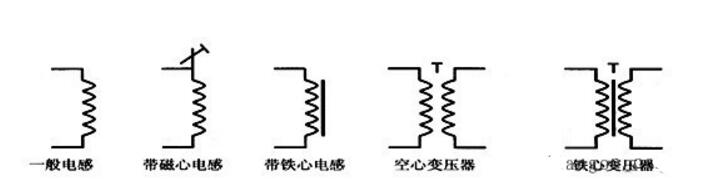
**Features**: Inductors allow DC to pass easily but oppose AC. The higher the frequency, the greater the opposition (inductive reactance).
**Function**: Inductors are used for filtering, tuning, impedance matching, and energy storage in switching power supplies. They are also used in LC circuits for resonance.
**Testing**: Use a multimeter in resistance mode. A good inductor will show a low resistance (equal to the wire’s resistance) and no open circuit. If it shows zero resistance, it may be shorted.
**Units**: Inductance is measured in henries (H), millihenries (mH), and microhenries (μH).
---
**Fourth, Power Transformer Code: B**
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It consists of primary and secondary coils wound around a core made of silicon steel.
**Principle**: When an AC voltage is applied to the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the secondary coil. Transformers are used to step up or step down voltages.
**Symbol**:
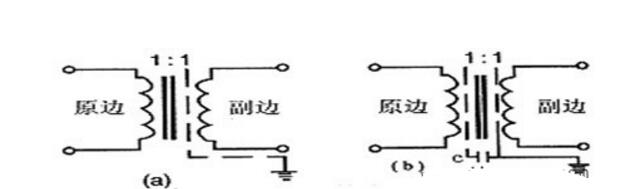
**Turns Ratio**: The relationship between input and output voltages is given by N1/N2 = V1/V2, where N is the number of turns in each coil.
**Power Transfer**: In an ideal transformer, input power equals output power. However, real transformers have losses, and efficiency ranges from 70% to 90%.
---
**Fifth, Diode Code: D or BG**
A diode is a semiconductor device with two terminals, P and N, that allows current to flow in only one direction. Common types include rectifier, Zener, LED, photodiode, and switch diodes.
**Function**: Diodes are used for rectification, voltage regulation, switching, and light emission (in LEDs).
**Testing**: Use a multimeter in the diode test mode. A good diode will show a forward voltage drop (around 0.6–0.7V for silicon, 0.3V for germanium) and infinite resistance in reverse.
**Polarity**: The black probe of the multimeter usually indicates the positive terminal.
**Symbol**:
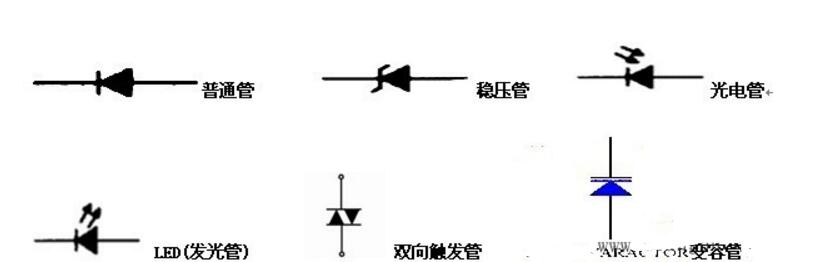
**Zener Diode**: Used for voltage regulation. It conducts in reverse when the breakdown voltage is reached.
**LED**: Emits light when current passes through it. Must be used with a current-limiting resistor.
**Photodiode**: Converts light into electrical current. Used in sensors and optical communication.
**Bidirectional Trigger Diode**: Used to trigger thyristors. Has high resistance in both directions unless triggered.
---
**Sixth, Thyristor Code: BCR**
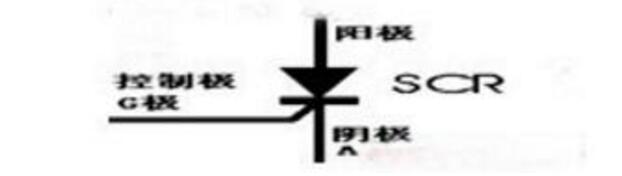
A unidirectional thyristor (also known as an SCR) is a semiconductor device that conducts current only in one direction. It has three terminals: anode (A), cathode (K), and gate (G).
**Function**: Used for AC and DC power control, such as in motor speed control and lighting systems.
**Testing**: A good thyristor will show infinite resistance between A and K in both directions. The resistance between G and K should be around 3–9kΩ.
**Operation**: The thyristor must have a forward voltage across A-K and a gate signal to turn on. Once triggered, it remains on until the current drops below the holding level.
**Symbol**:
---
**Seventh, Triac Code: SCR**
A triac is a bidirectional thyristor that can conduct current in both directions. It is commonly used in AC control circuits.
**Function**: Used in dimmers, motor speed controls, and AC switches.
**Electrodes**: Triacs have three terminals: T1, T2, and G (gate). Unlike SCRs, they do not distinguish between anode and cathode.
**Testing**: A good triac will show high resistance in both directions. The resistance between G and T1 should be around tens to hundreds of ohms.
**Symbol**:

---
**Eighth, Transistor Code: BG or Q, V, T**
A transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device used for amplification and switching. There are two main types: NPN and PNP.
**Function**: Used in amplifiers, oscillators, and digital logic circuits. It can amplify current or act as a switch.
**Testing**: Use a multimeter in resistance mode. A good transistor will show low resistance between B-E and B-C in one direction, and high resistance in the other.
**Polarity Identification**: The base can be identified by measuring resistance between all pairs. The terminal with the lowest resistance is the base.
**Symbol**:
**Types**: Transistors come in different sizes (small, medium, large power) and frequencies (low, high). Their gain (β) increases with temperature.
This content has been rewritten and expanded to ensure clarity, accuracy, and a natural, human-like tone.
Cooling Film
"Cooling Film" typically refers to a type of material designed to reduce heat buildup, often used in electronic devices, buildings, or vehicles. These films can work through various mechanisms such as reflecting sunlight, dissipating heat more efficiently, or insulating against external heat sources. They can be made from different materials and are applied in various ways depending on their intended use.
For example:
- **Electronic Cooling Films:** These are often used in smartphones, laptops, and other electronic devices to help manage heat generated by internal components. They might be applied directly to the surface of a device or integrated into heat sinks.
- **Building Cooling Films:** Applied to windows or exterior surfaces, these films can reflect a portion of the sun’s heat away from the building, helping to keep interiors cooler.
- **Automotive Cooling Films:** Used in car windows or on the vehicle's body to reduce the amount of heat entering the cabin.
If you have a specific application or context in mind for "Cooling Film," please provide more details so I can offer more targeted information!
self-cleaning radiative,Energy saving,cooling film,radiative cooling,ultra-high solar reflectivity,Car window cooling film
ZHONG HAN INTERNATIONAL TRADE CO., LTD , https://www.cck-ht.com






